Contract labor in India is a key component of the economy, especially for MSMEs operating in construction, infrastructure, and manufacturing sectors. Businesses hire workers through third-party contractors to quickly increase staff, reduce costs, and stay competitive. However, strict compliance with labor laws is essential. The Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970 (CLRA Act India) governs contract labor to protect workers and ensure fair treatment. Every employer should fully understand this act and adhere to its provisions.
When Does the CLRA Act Apply?
The CLRA Act applies to companies that have employed twenty or more contract workers in the last twelve months. Once covered under this act, a company acting as the principal employer must secure a registration certificate from the relevant labour department. Likewise, contractors supplying workers are required to obtain a valid license. Operating without registration or a license is illegal and exposes businesses to legal risks. Proper registration of contract workers in India is the foundational step toward compliance.
Responsibilities: Contractor vs. Principal Employer
A frequent misunderstanding involves the division of responsibilities between contractors and principal employers. The contractor handles recruitment, payment, and supervision of workers. They must pay wages on time, provide welfare amenities such as canteens, restrooms, drinking water, and first aid, and comply with PF and ESI requirements.
The principal employer, the MSME or company, holds a shared responsibility to ensure compliance. If contractors fail to meet legal obligations, the principal employer is held liable.
This dual responsibility is why contracts with labor suppliers need clarity, and regular compliance checks are crucial. Indian courts reaffirm that principal employers cannot evade their obligations toward contract labor.
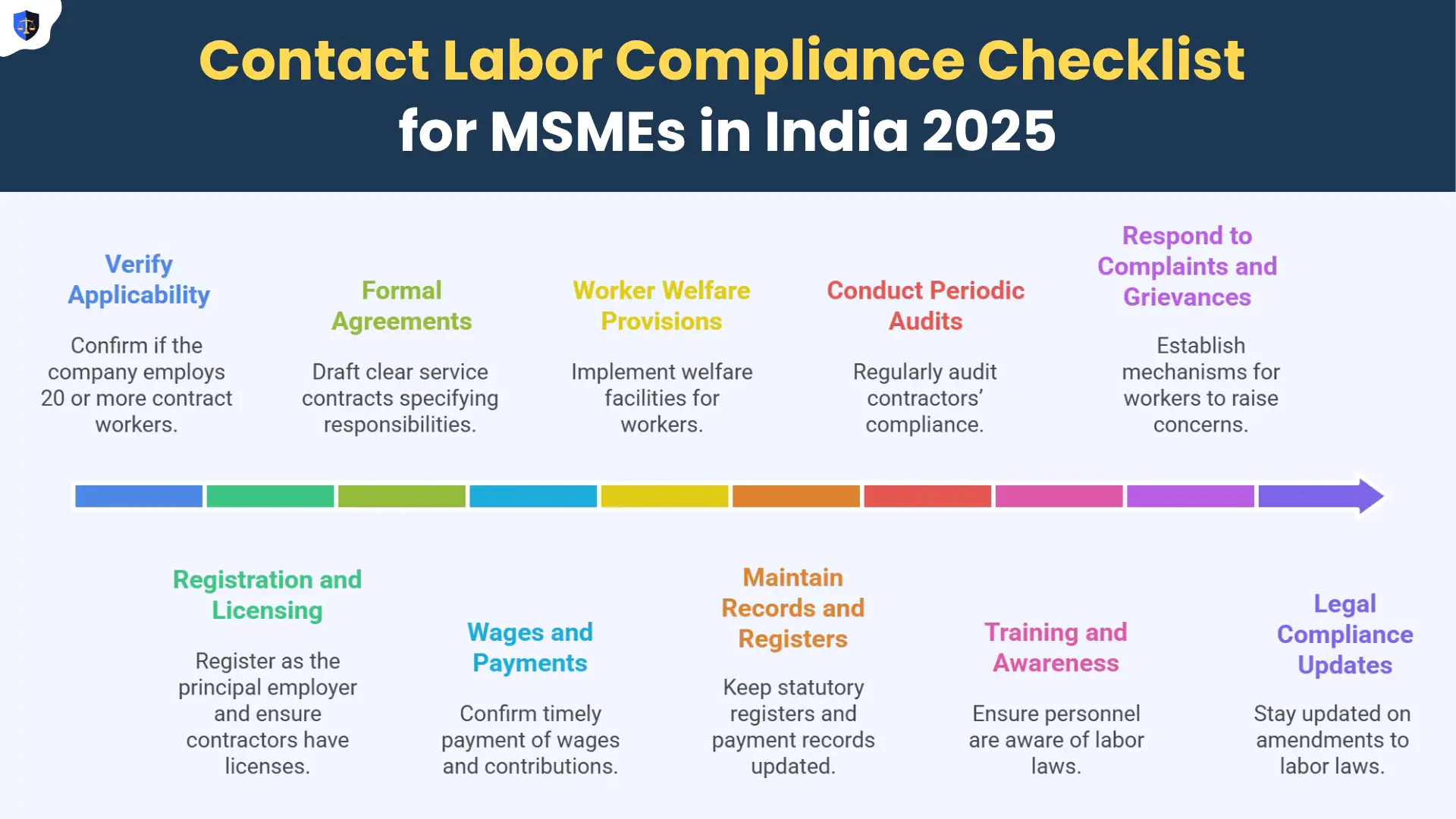
Check our complete Contract Labor Compliance Checklist to ensure your MSME meets all legal requirements effortlessly.
Rights of Contract Workers Under Indian Law
Contract workers possess several legal rights that employers must respect. These include:
• Timely payment of wages,
• Equal pay for equal work,
• Freedom from discrimination,
• Access to essential welfare facilities including toilets, drinking water, and medical care.
They are covered by various laws such as the Payment of Wages Act, Minimum Wages Act, Employees’ Provident Fund Act (EPF), and the Employees’ State Insurance Act (ESI).
Contract employment does not exempt workers from these protections, and MSMEs must honor these rights to avoid violations.
Key Compliance Steps for MSMEs
To manage contract labor in India effectively and avoid penalties, MSMEs need to:
• Register as the principal employer as per the CLRA Act when the threshold of twenty contract workers is reached.
• Engage only licensed contractors.
• Maintain all necessary documents and registers accurately and up to date.
• Ensure welfare services are consistently available to contract workers.
• Confirm contractors fulfill requirements related to PF, ESI, and minimum wages.
• Conduct periodic audits and inspections of contractor compliance to minimize risks.
• Maintain detailed records of compliance to handle audits or disputes smoothly.
• Many smaller enterprises find it difficult to keep up with these rules.
Contractors might delay wages, skip PF payments, or fail to maintain the necessary records. When these mistakes happen, it is the principal employer who becomes legally responsible, often facing unexpected financial penalties and legal complications.
Because of this, MSMEs should draft clear service agreements that define responsibilities precisely and regularly monitor contractors for compliance.
Taking these steps is not just about avoiding legal trouble; it reflects good employer responsibility and ethics.
Takeaway
Strong POSH Act compliance is key to making workplaces safe and respectful for everyone. Organisations should regularly check how well they follow the law, support their Internal Complaints Committee, and keep employees informed and confident to speak up. Acting early and with commitment not only meets legal requirements but also builds a trusting work culture where dignity and respect come first.
Start your POSH compliance audit today with HR Legal Experts to build a trusted, safe workplace for all.
FAQs: Contract Labor in India
Contract Labor Compliance Questions
It applies when a company employs or has employed 20 or more contract workers in the past 12 months. Registration and licensing are then mandatory.
Yes, but contractors and principal employers must ensure that contract laborers get equal wages and welfare as permanent staff doing similar work.
The principal employer is legally responsible if the contractor fails to fulfill wage payments or statutory contributions.
There is no official limit, but full reliance on contract labor may lead to legal scrutiny and risks, especially if contract labor replaces permanent jobs.
Penalties include fines and imprisonment, with continuous violations attracting additional fines per day until corrected.

HR Legal Experts is a specialized consulting firm helping businesses stay fully compliant with labour laws and HR policies. With a proven track record of serving 500+ organizations, we deliver customized solutions in POSH compliance, employee handbooks, contracts, and regulatory documentation. Our team combines legal expertise with practical HR insights to ensure risk-free, people-first workplaces.